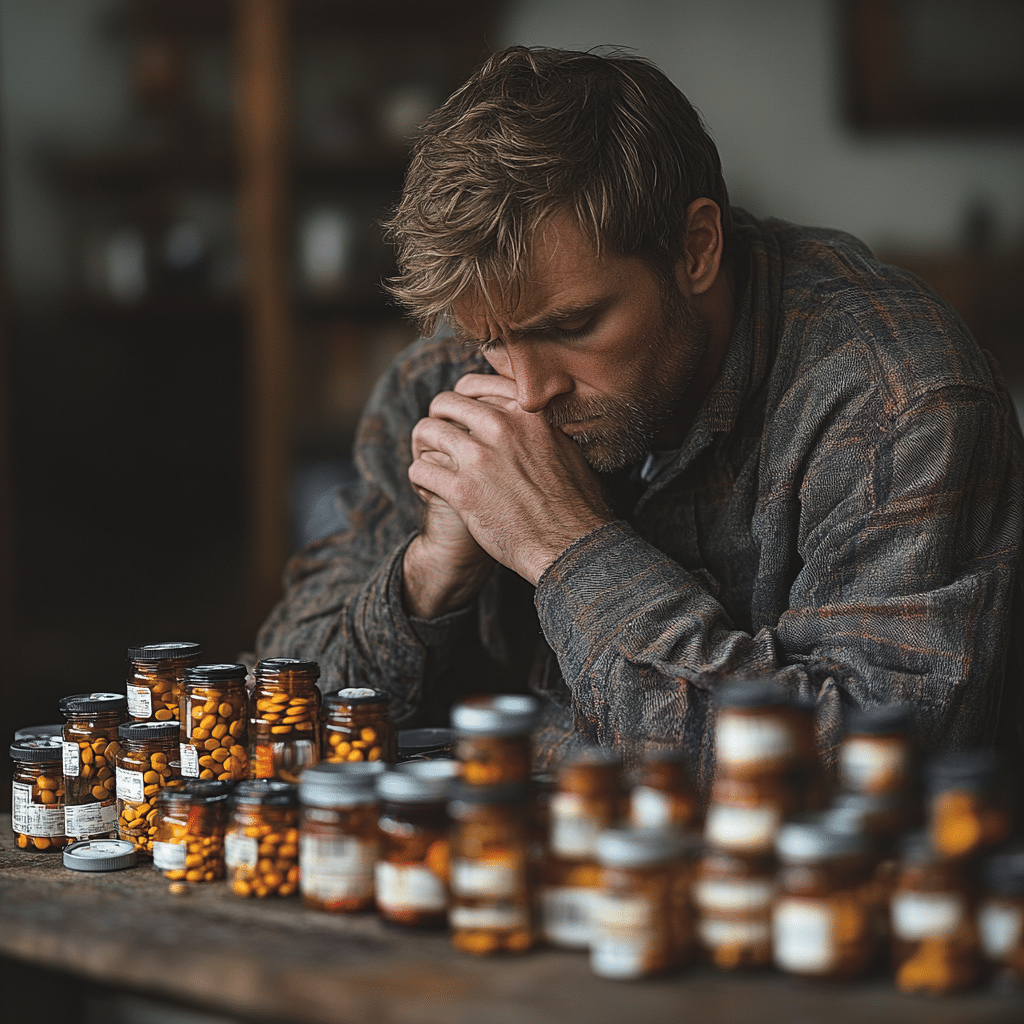
In recent years, addiction in rural communities has become an insidious and growing crisis, overshadowed by the more visible struggles in urban areas. However, the effects in these rural regions are equally, if not more, devastating. This article explores the unique challenges rural areas face, shares heart-wrenching stories from those affected, and spotlights innovative solutions that bring hope. We’re shining a light on an urgent problem that needs immediate attention.
Challenges of Addressing Addiction in Rural America
Limited Access to Healthcare and Rehabilitation Services
One of the biggest hurdles in addiction in rural communities is the lack of accessible healthcare and rehab services. In places like Wyoming and Montana, people often live hundreds of miles from the nearest treatment facility. This extensive distance forces individuals either to make arduous journeys or to skip treatment entirely. Think about it: a person struggling with addiction might not have the means or the emotional strength to travel that far for help.
Socioeconomic Barriers
Economic hardship is another significant challenge. Rural areas frequently wrestle with higher poverty rates and fewer job opportunities. These socioeconomic strains heighten addiction issues as people turn to substances as an escape. The opioid crisis in Appalachia is a prime example, fueled in large part by economic despair. Here, individuals often seek cash loan to meet basic needs, and the cycle of debt and dependency deepens.
Stigma and Secrecy
In tight-knit rural communities, the stigma surrounding addiction in rural communities can be paralyzing. The fear of social ostracism keeps many from seeking help, leading to a cycle of secrecy and isolation. Families suffer in silence, scared to reach out for fear of judgment. This lack of openness prevents people from accessing the support they desperately need.
Real-Life Impact: Stories from the Heartland
The Case of Manchester, Kentucky
Take Manchester, Kentucky, for example. Dubbed the “City of Hope,” this town was hit hard by the opioid epidemic. Yet, its transformation has been phenomenal. Community-led initiatives have turned the tide, establishing support groups, awareness programs, and even opening a local rehab center. The story of Manchester underscores the power of collective action and community support in tackling addiction in rural communities.
The Personal Journey of Jessica Love
Jessica Love, a mother from rural Ohio, lost her son to heroin addiction. Her journey from unimaginable pain to advocacy showcases the need for compassionate, localized support networks. Jessica became a cornerstone in her community, leading neighborhood-based intervention programs and support groups designed specifically for the unique challenges of addiction in rural communities. Her story is a poignant reminder of love and resilience even in the darkest of times.
| Topic | Urban Areas | Rural Areas |
| Perception of Drug Use | Often seen as predominant | Increasing and often more prevalent |
| Prevalent Substances | Cocaine, heroin, synthetic drugs | Prescription opioids, methamphetamine, alcohol |
| Adolescent Use | Lower alcohol use rates | Higher alcohol use rates, more binge drinking |
| High-Risk Behaviors | Lower incidence of DUI among youth | Higher incidence of DUI among youth |
| Community Engagement | Higher engagement in activities | Decreased involvement due to stigmatization |
| Stigma | Moderate social stigma | High social stigma, leading to alienation |
| Access to Treatment | More facilities and options | Limited availability and access to treatment |
| Economic Factors | Varied socio-economic conditions | Lower average income, higher unemployment |
| Healthcare Resources | Better access to healthcare | Limited healthcare resources and support |
Innovative Solutions and Grassroots Efforts
Telehealth and Remote Counseling
Telehealth is emerging as a crucial tool to bridge the healthcare gap in rural areas. Organizations like the Hazelden Betty Ford Foundation are expanding their virtual counseling services, making it easier for people in rural communities to access addiction therapy without long commutes. This innovation offers a lifeline to those who might otherwise forego treatment due to transportation hurdles.
Mobile Health Clinics
Mobile health clinics have been another game-changer. Boston Medical Center’s “Curb the Crisis” initiative brings healthcare directly to areas hardest hit by addiction. These clinics offer on-the-spot treatment, including medication-assisted therapy, making immediate and potentially lifesaving interventions possible. Bringing healthcare to the people, rather than the other way around, is proving to be incredibly effective.
Faith-Based and Community Programs
Faith-based organizations play a crucial role, particularly in rural settings. Programs like Celebrate Recovery, run out of local churches, provide not just spiritual, but also practical support for those in addiction recovery. These community-focused solutions help in addressing the stigma many people face, making it easier for them to seek and receive help.
Looking Forward: The Road to Recovery in Rural Communities
The fight against addiction in rural communities demands multi-faceted approaches tailored to these areas’ specific challenges. Expanding telehealth services, empowering grassroots initiatives, and fostering community solidarity are vital steps. By doing so, we can create a future where everyone, regardless of their location, has access to the help they need.
The resilience and innovative spirit of rural communities stand as a beacon of hope, demonstrating that even in the darkest times, there is a way forward. By highlighting these stories and efforts, we not only bring attention to this hidden crisis but also inspire broader support and more effective action in combating addiction across rural America.
For more information on how to support parents of children struggling with addiction or those who have lost a child to addiction, visit Mothers Against addiction.
Addiction in Rural Communities: Hidden Crisis
Addiction in rural communities isn’t always discussed, but it’s a growing concern that calls for our attention. Did you know that these communities often face unique challenges compared to urban areas? Access to healthcare services, social stigma, and limited support networks can all exacerbate the crisis.
Unique Considerations
Interestingly, the ties between addiction and financial stress are striking. For instance, historical mortgage interest rates have occasionally placed extra pressure on households, sometimes contributing to substance abuse. Imagine trying to fight addiction while also coping with fluctuating mortgage financial rates—it’s a steep hill to climb. These financial strains can make it even harder for residents to seek help and recovery.
Impact on Diverse Demographics
Moreover, addiction in rural communities doesn’t spare anyone and can be shockingly prevalent in minority groups. These individuals often face greater hurdles due to systemic inequalities and a lack of culturally competent resources. Here’s an intriguing fact: addiction in minority Communities often goes hand-in-hand with poor access to tailored treatment options. This makes the push for inclusive programs more critical than ever.
Broader Spectrum of Issues
And let’s not forget—Lgbtq+ addiction Issues are also a significant part of the conversation. Rural areas often lack specialized support for these groups, compounding the isolation and difficulty in finding safe, affirming care. It’s a hidden crisis begging for more awareness and resources. Amid these struggles, seemingly minor trivia, like a Kansas license plate being a symbol of pride for local residents, might seem trivial, but they often represent a sense of identity and hope to hold on to.
Evaluating the Situation
To wrap things up, understanding What Does The value mean in terms of community support can be vital. Everyone from policymakers to grassroots organizations needs to consider the broader impacts addiction has on rural communities to pave the way for effective solutions. The numbers, the stories, and the trivia all wrap together to paint a picture that demands our attention, compassion, and immediate action.
Is substance abuse higher in rural areas?
Substance abuse is on the rise in rural areas, sometimes even more than in urban areas. This is a growing concern and differs from the common perception that drug problems are mainly an urban issue.
Is alcoholism more common in rural areas?
Alcohol use among rural adolescents and young adults is higher, and they tend to engage in riskier behaviors like binge drinking and driving under the influence more often than those in urban areas.
What effect does substance abuse have on communities?
Substance abuse can severely impact communities by increasing rates of crime, reducing productivity, and straining healthcare resources. It also alienates users from their families and community activities, diminishing the overall social fabric.
How to prevent drug abuse in a community?
Preventing drug abuse in a community involves increasing awareness, providing education programs, improving access to mental health services, and promoting healthy activities that engage youth and adults alike.
Is there more abuse in rural areas?
Recent trends indicate a rising issue of substance abuse in rural areas, even surpassing urban areas in some instances.
What is the overdose rate in rural vs urban communities?
The overdose rate comparison varies, but rural areas are seeing increasing rates which often outpace those in urban settings due to fewer healthcare resources and delayed emergency response times.
What state has the highest alcoholism?
The state with the highest alcoholism rates can change from year to year, but states with harsh climates or those with higher stress levels often top the list.
What city in the U.S. has the highest rate of alcoholism?
Cities known for high rates of alcoholism are often large metropolitan areas with heavy drinking cultures, but these can shift over time based on local policies and economic conditions.
Where do most alcoholics live?
Alcoholics are found everywhere, but higher rates are often seen in places with stressful lifestyles, less access to healthy activities, and more acceptance of heavy drinking.
What are the causes of drug abuse in the community?
Key causes of drug abuse in communities include peer pressure, lack of education, economic stress, and easy access to substances.
What are the factors that influence drug abuse in our communities?
Factors influencing drug abuse in communities often involve socio-economic stress, family relationships, availability of drugs, and mental health issues.
What are the social effects of drug addiction?
Social effects of drug addiction range from increased crime to broken families, unemployment, and a general decline in community well-being.
How to solve drug addiction?
Solving drug addiction requires a multifaceted approach, including strong community support, accessible treatment options, and comprehensive education programs.
How to control addiction?
Controlling addiction involves a combination of medical treatment, counseling, support groups, and sometimes lifestyle changes to avoid triggers.
What are 5 ways drug abuse can be curbed?
Ways to curb drug abuse include increasing education and awareness, providing accessible rehab facilities, enacting stricter laws, promoting healthy lifestyles, and offering strong support networks.
What is a comparison of rural and urban substance abuse treatment admissions?
Treatment admissions for substance abuse show different patterns in rural and urban areas, with rural areas often lacking sufficient nearby treatment facilities, leading to longer travel times and less frequent admissions.
What state has the highest substance abuse problem?
States with the highest substance abuse problems often face a combination of socio-economic challenges and limited access to mental health care.
Which factors contribute the most to substance abuse?
Environmental stress, mental health issues, peer pressure, and socio-economic factors contribute significantly to substance abuse.
What are the demographic factors in the use and abuse of substance?
Demographic factors in substance use and abuse include age, income level, education, and geographic location, with varying impacts across different communities.