Addiction is a formidable challenge, affecting not just individuals but also their families and communities. Beyond the devastating personal costs, addiction carries significant, often hidden financial burdens. In this article, we will delve into the various financial implications of addiction, exploring direct and indirect costs through real-world examples and statistical analyses.
Direct Financial Impact of Addiction
Medical and Healthcare Expenses
The cost of treating addiction can be astronomical. Medical treatments, like detoxification, rehabilitation, and ongoing therapies, quickly add up. For instance, a month-long stay at the Betty Ford Center—a renowned rehab facility in Rancho Mirage, California—can cost upwards of $37,000. Moreover, subsequent outpatient treatments and medications like Methadone or Buprenorphine, used in opioid addiction, accumulate additional expenses over time.
Legal Fees and Court Costs
Addiction often leads to legal troubles, including arrests for possession, DUI, or theft to support the habit. Legal fees can mount rapidly. A DUI in Los Angeles can cost an offender approximately $10,000 in fines, legal fees, and increased insurance premiums. Additionally, families might find themselves paying for ongoing legal representation and court-mandated programs.
Indirect Financial Impact of Addiction
Loss of Productivity and Employment
Addiction severely impacts an individual’s ability to maintain steady employment. Absenteeism, decreased performance, and eventual job loss are common consequences. According to the National Safety Council (NSC), the cost to employers due to addiction-related productivity loss was around $81 billion in 2023 alone. This loss permeates the economy, affecting businesses and creating a ripple effect.
Increased Insurance Premiums
Individuals struggling with addiction might find their health insurance premiums rising. Substance abuse disorders lead to a higher incidence of claims, prompting insurance companies to increase rates for the insured and sometimes their families. An average family health plan might see premiums increase from $20,000 to $24,000 annually due to these additional claims.
| Category | Details | |
| Government Drug Enforcement Policies | Involves costs related to law enforcement, legal proceedings, incarceration, and rehabilitation programs. | |
| Lost Human Productivity | Lost wages and decreased production due to absenteeism, poor job performance, and premature deaths. | |
| Job Performance Impacts | Increased likelihood of reduced performance, job loss, and difficulties in finding new employment. | |
| Preventable and Treatable Condition | Although treatable, a substantial number of resources are required for prevention and treatment. | |
| Societal Costs | ~6% of the nation’s income; over $532 billion per year. | |
| Workplace Costs | Decreased productivity, increased healthcare expenses, and higher rates of workplace accidents. | |
| Healthcare Expenditure | Increased costs for emergency treatments, long-term healthcare, and rehabilitation services. | |
| Criminal Justice System Costs | Expenses related to law enforcement, court proceedings, and incarceration. | |
| Cost Component | Amount | |
| Law Enforcement and Incarceration | Billions of dollars annually | |
| Lost Wages (due to absenteeism, job loss) | Significant portion of $532 billion societal costs | |
| Healthcare (Emergency and Long-term) | Billions annually | |
| Productivity Loss (Estimated Percentage) | ~4-5% of GDP | |
| Rehabilitation and Treatment Services | Hundreds of millions to billions annually | |
| Premature Deaths | Tangible and intangible costs including lost potential earnings | |
| Feature | Price/Cost | Benefits |
| Comprehensive Treatment Programs | Variable (Insurance, Out-of-pocket) | Improves health, enhances productivity, reduces long-term societal costs. |
| Prevention Programs in Schools/Workplaces | Government and private funding | Decreases initiation rates, educates about risks, reduces future treatment costs. |
| Support for Families and Communities | Mostly covered by Non-profits and Government | Mitigates the emotional and financial impact on families, supports community resilience. |
| Legislative Measures to Control Substance Abuse | Government-funded | Effective regulation reduces accessibility, prevents new cases of addiction. |
Societal and Community Costs
Burden on Public Resources
Addiction stretches public resources thin. Emergency services, including ambulance and first responder calls, often deal with overdose cases. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) reported that overdose-related emergency calls cost taxpayers roughly $12 billion in 2023. Overcrowded public hospitals, long wait times, and strained community outreach programs add to these hidden costs.
Impact on Family Finances
Families of individuals struggling with addiction face their own financial tolls. Directly supporting a loved one’s recovery can drain savings and increase debt. Additionally, co-signing loans or mortgages that later default results in families absorbing the debt. Take the case of Jim, whose parents cashed out their retirement savings to pay for multiple rehabilitation attempts, underscoring the profound financial strain on families.
Societal Cost of Incarceration
Incarceration and the Penal System
Addiction-related crimes result in imprisonment, incurring society vast expenses. Housing an inmate costs an average of $31,000 per year, with some states like California spending up to $75,000 per inmate annually. For drug offenders, alternative treatments like rehabilitation might be more cost-effective, saving both money and lives.
Long-Term Economic Impact
Education and Lost Opportunities
Youth addiction disrupts education, leading to long-term economic consequences. High school dropouts earn significantly less than their peers, contributing less to the economy. For former addicts, the struggle to catch up educationally and professionally often leads to lower lifetime earnings.
Housing and Homelessness
Addiction is a significant factor in homelessness, creating additional financial pressure on public housing systems and shelters. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) estimated that addiction-related homelessness cost the public at least $32 billion in 2023, factoring in shelter, emergency services, and social work.
Innovative Approaches to Mitigating Financial Impact
Comprehensive Rehabilitation Programs
Investing in comprehensive rehabilitation programs can reduce the long-term financial impact of addiction. Programs like those offered by Hazelden Betty Ford Foundation integrate medical treatment, therapy, and post-rehabilitation care, improving recovery rates and reducing related costs.
Community Support and Education
Strengthening community support systems and providing education on addiction can preempt some of its financial impacts. Getting involved in programs like Parents Against Drugs (P.A.D.) can provide families with resources and advocacy, helping them cope with an addicted child and seek comprehensive support.
Recognizing and addressing the financial impact of addiction requires a holistic approach. By understanding these hidden costs and investing in prevention, treatment, and recovery programs, we can lessen the financial burden on individuals, families, and society at large. Tackling addiction is not just a health imperative but an economic necessity. It’s time we took a closer look at the numbers and their profound implications.
For more on coping With an addicted child, visit Mothers Against Addiction. If you need to understand the challenges surrounding addiction and divorce, see Divorce And Addiction. Moreover, to educate yourself and your family on addiction, explore our Addiction Education For Families resources.
By addressing these hidden costs head-on, we can work towards a future where families are better supported, communities are stronger, and the financial burden of addiction is significantly reduced.
(Tag: Financial impact of addiction, Addiction education for families, Coping with an addicted child, Divorce and addiction, Social security office Tulsa, How much Does a notary make, Carmen Electra Movies And TV Shows, Sonic running, Reincarnated as a sword season 2.)
Disclaimer: This article may include references to statistical data and real-life examples; for further detailed information, please visit our Mothers Against Addiction website.
Financial Impact of Addiction: Hidden Costs
The Obvious Costs
When thinking about addiction, the direct cost of substances( often pops up first. Whether it’s alcohol, prescription drugs, or illicit substances, users spend significant amounts of money. You might be surprised to learn that, on average, Americans spend over $90 billion annually on alcohol alone. Stretching this over time, those “casual” expenses suddenly turn into life-changing sums, crippling financial stability.
Health-Related Expenses
Another major financial burden is healthcare. Did you know that alcohol-related healthcare costs( exceed $249 billion yearly in the United States? This includes not only direct medical treatment for conditions caused by addiction but also rehabilitation, therapy, and even long-term care. For families already trying to cope emotionally, the stress of medical bills can be overwhelming, sometimes forcing them into debt.
Lost Productivity and Employment Issues
It’s not just the individuals suffering from addiction who feel the pinch; employers and the economy take a hit too. Each year, lost productivity related to addiction( costs American businesses $81 billion. This statistic takes into account absenteeism, reduced performance, and job loss. Imagine the ripple effects: lower income for families, fewer opportunities for career growth, and increased strain on social services.
Legal and Criminal Justice System
The financial impact of addiction doesn’t stop at health and employment. The legal costs are another load families often bear. Criminal justice involvement( related to drug use, including arrests, court fees, and incarceration, weighs heavily on both public resources and personal finances. The American criminal justice system spends millions on addiction-related cases each year, a stark reminder of the broader repercussions.
By weaving these hard-hitting, real-world costs into the lived experiences of individuals and families, we paint a fuller, more impactful picture of the true financial impact of addiction. There’s no dodging the fact; the hidden costs stretch far and wide, embedding themselves deep into both personal lives and society at large.
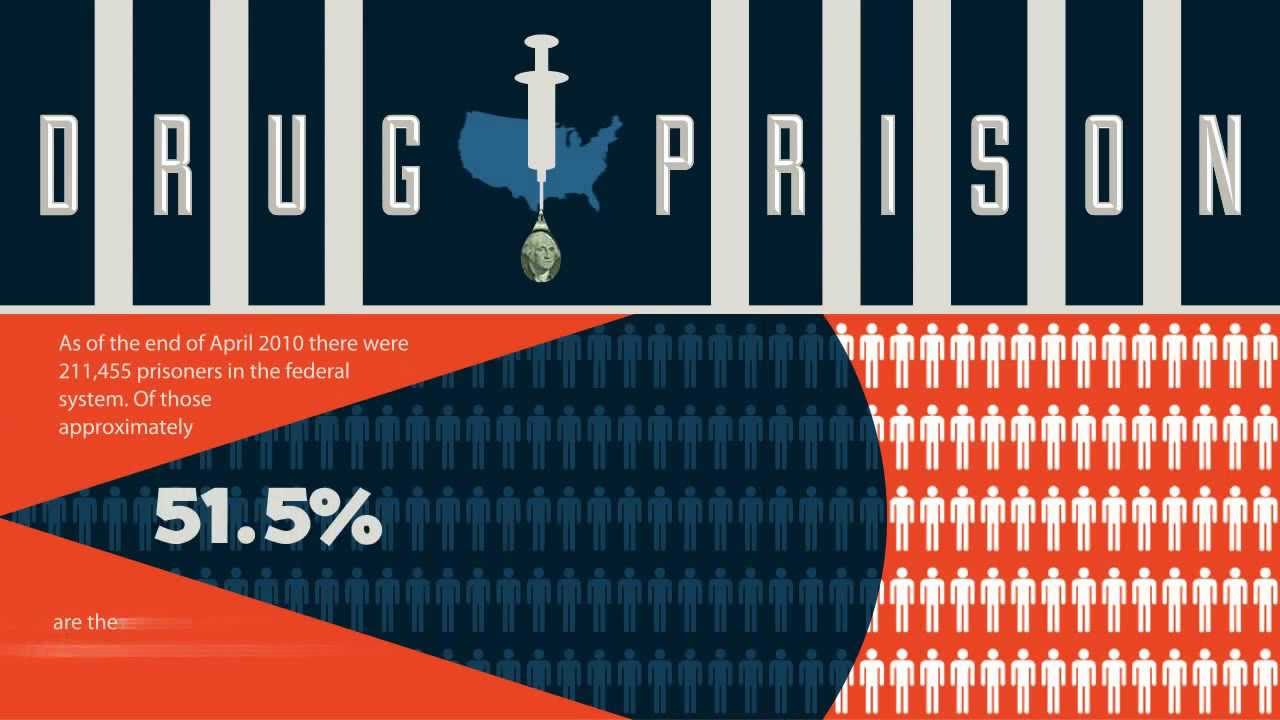
What are the economic effects of drug abuse?
Drug abuse hits the economy in two main ways: the cost of government measures to fight drug-related issues and the drop in productivity when people can’t work or die early because of drug problems.
Why does addiction lead to poverty?
Addiction often leads to poor work performance, which can get someone fired. Once fired, it’s tougher to find new jobs, piling on stress and making relapse more likely, thus feeding the cycle of poverty.
What is the impact factor of addiction?
Addiction can ruin work performance, relationships, and health. This lowers income, increases job loss, and mounts healthcare costs, putting a financial strain on families and society.
What is the economic burden of substance abuse?
Substance abuse costs the U.S. over $532 billion annually in healthcare, lost productivity, and law enforcement. This sum is nearly six percent of the nation’s income, showing the massive financial toll.
What is the economic impact of overdose?
Overdoses add to the economic burden by racking up emergency medical costs, reducing the workforce, and causing heartache for families, which can translate into further societal costs in healthcare and other support services.
What are the economic effects of alcoholism?
Alcoholism drives up healthcare costs due to treatment for liver diseases, accidents, and other related health problems. It also leads to lost wages and productivity, impacting the broader economy.
What is the vulnerability of addicts?
Addicts often face job loss, legal troubles, and health issues, making them more vulnerable to poverty and social isolation. These struggles make it harder to break the cycle of addiction.
What are the social effects of drug abuse?
Drug abuse harms social dynamics by wrecking families, causing crimes, and increasing healthcare use. Communities bear these burdens through heightened safety concerns and financial strains.
Why do people become love addicts?
Love addiction happens when someone craves love and affirmation, often stemming from past trauma or low self-esteem. It can cause unhealthy relationship patterns, affecting emotional well-being.
What are the effects of addiction?
Addiction harms health, costs jobs, breaks up families, and taps into healthcare resources. This mess impacts everyone from the addict to their loved ones and society as a whole.
What are 5 risk factors for addiction?
Five risk factors for addiction include genetic predisposition, early substance use, mental health issues, lack of support, and environments that encourage drug use.
What is the most important factor in Substance Abuse?
The most vital factor in substance abuse is early intervention and support. Catching issues early and having strong support systems can prevent full-blown addiction.
What are the social and economic factors of drug abuse?
Drug abuse carries social costs such as crime, family breakdowns, and healthcare burdens. Economically, it leads to lost productivity, increased law enforcement costs, and strained medical services.
What is the economic value of drugs?
Drugs have a tricky economic value. While the illegal trade can generate massive profits for traffickers, the public cost in healthcare, lost productivity, and criminal justice efforts is staggering.
What is the economic burden of chronic diseases?
Chronic diseases like those from substance abuse cause ongoing medical expenses, productivity loss, and early deaths, which all add to economic stress on families and the healthcare system.
What are the effects of economic abuse?
Economic abuse happens when one person controls another’s access to economic resources, leading to financial dependence and instability. This often accompanies other forms of abuse and limits personal freedom.
What is the economic value of drugs?
Legalizing drugs can boost the economy through tax revenues and reduced law enforcement costs, but it might also lead to higher healthcare and social costs if abuse increases.
How does drug legalization affect the economy?
Medicine impacts the economy by saving lives and boosting productivity, but high costs can be a burden. Efficient healthcare and affordable medicines are key to a balanced economic impact.