Wet Brain Meaning and Its Place in Medical Terminology
Cracking open the conversation on alcohol-related health ailments, we delve into the murky waters of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, or as it’s informally known, “wet brain.” This condition signifies severe neurological chaos, springing from a dearth of vitamin B1, otherwise known as thiamine. This deficit predominantly besieges chronic drinkers, weaving Wernicke’s encephalopathy with Korsakoff’s psychosis into a dire tapestry of brain impairment. In medical jargon, wet brain is more than a colloquial whisper; it’s a heavyweight contender in discussions of neurological well-being.
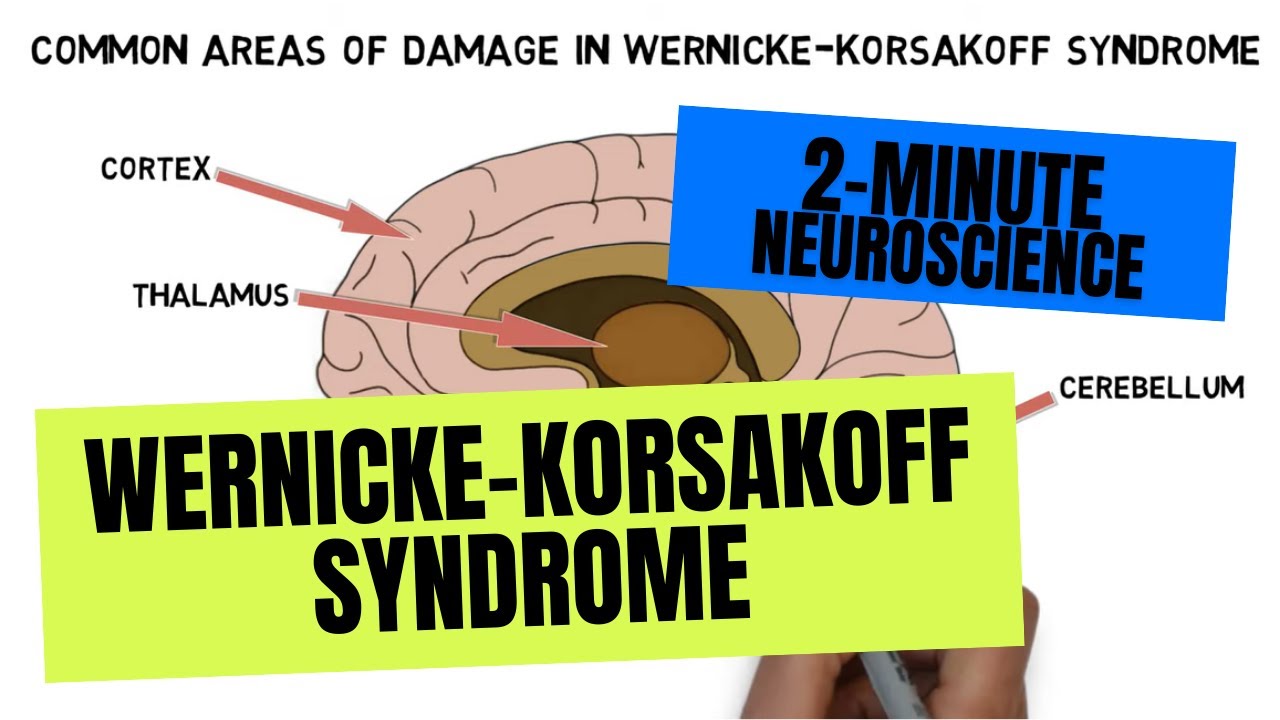
The Pathophysiology of Wet Brain Syndrome
Unpacking the nuts and bolts of this condition tells a tale of thiamine—a VIP nutrient that the brain craves for its metabolic shindigs. When alcoholism crashes the party, it swipes the invites and thiamine gets ousted from the bash. This ousting sabotages the brain’s energy production, tossing neurons into a tailspin. We’re talking a destructive domino effect—enzymes go on strike, cells start to sulk, and before you know it, the central nervous system is throwing a major fit.

| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Name of Condition | Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (WKS), also known as “wet brain” |
| Cause | Thiamine (Vitamin B1) deficiency |
| Commonly Associated With | Long-term, heavy alcohol consumption and poor nutrition |
| Acute Phase | Wernicke’s encephalopathy – characterized by confusion, loss of muscle coordination (ataxia), and abnormal eye movements |
| Chronic Phase | Korsakoff syndrome – involves severe memory impairment and confabulation (making up stories) |
| Symptoms | – Confusion and disorientation – Muscle coordination problems – Eye movement disturbances – Memory loss – Hallucinations |
| Diagnosis | Based on symptoms and history of dietary insufficiency. Medical tests (MRI, blood tests for thiamine levels) to confirm |
| Treatment | Immediate thiamine replacement, alcohol abstinence, and nutritional support |
| Reversibility | – Wernicke’s encephalopathy: partially or fully reversible with prompt treatment – Korsakoff syndrome: often irreversible with potential for permanent brain damage |
| Life Expectancy | – Variable; 50% chance of 8-year survival after diagnosis – Earlier diagnosis and treatment can potentially improve prognosis |
| Complications | – Continued cognitive decline – Problems with walking and balance – Permanent memory impairment |
| Prevention | – Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption – Maintaining a balanced diet with sufficient thiamine intake |
| Further Notes | Despite the severity, awareness and early recognition can lead to better management and improved outcomes for sufferers |
Early Wet Brain Symptoms and Diagnosis
Say, ever had a bit too much to drink, a real spinning-room soirée? Imagine that as the sneak peek trailer for wet brain. Early symptoms—confusion, a wobbly gait, and eyes darting like they’re watching a tennis match—are often shrugged off as just another hangover. But lo and behold, these could be the early warning shots fired by wet brain. Picture the diligence of Dr. Annika Smith, a neuropsychiatrist with a keen eye for addiction’s subtleties, who emphasizes the urgency for prompt medical attention.

The Progression: What Is Wet Brain’s Impact on the Brain?
Stroll along wet brain’s gloomy timeline, and you’ll notice cognitive functions crumbling like a sandcastle at high tide. Initially, thiamine replenishment can mend the fences, reverting some of the damage. But let it fester, and you’re looking at permanent digs in the gray matter. Think less “senior moments” and more “long-term lease on forgetting street,” with the grim addition of coordination and vision issues.

Wet Brain Syndrome Treatment Protocols and Success Rates
Speaking of treatment, it’s a race against the clasp of wet brain’s cold fingers. Serve up thiamine on a silver platter early on, and you’ll save more than a few brain cells. But timing is like a ticking time bomb here, and success rates vary. Facilities like New Horizons Recovery toss the lifeline of early intervention into the sea of chronic alcoholism and reel in markedly better outcomes.
Living with Wet Brain: Real-life Experiences and Management Strategies
Now, let’s hear it straight from the horse’s mouth—those who wear wet brain’s heavy coat daily, or those who shoulder the weight of caring. They’ve got the scoop on nailing down a routine that keeps the gears grinding. From wrangling memory aids to tweaking home safety and nutrition—there’s an arsenal of day-to-day hacks that maintain a semblance of usual programming.
Long-Term Outlook: Wet Brain Syndrome Lifespan Considerations
If we peek at the data with our detective hats on, we see a palette of fates. For the wet brain crowd, the crystal ball is clouded, but one study sends a shiver down the spine, revealing that over half meet their maker within eight years. And if you’re crunching numbers, no sugar-coated statistic sweetens this lifespan insight, folks.
Pioneers in Wet Brain Research and Future Directions
Let’s tip our hats to the trailblazers, like Dr. Felipe Sierra, who’s strapping on his boots for the long trek toward breakthroughs. These beacons of hope in wet brain’s dusky landscape shine a light on novel treatments and prevention patrols, possibly rewriting what a wet brain diagnosis may spell in the future.
The Role of Advocacy Groups in Wet Brain Syndrome Awareness
You can bet your bottom dollar that battalions like Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD) aren’t sitting this one out. Their bullhorns amplify the hush around wet brain, fostering a squad of supporters and prodding the slumbering beast that is policy reform and research finance—all crucial moves in combating a grim prognosis.
Innovative Wrap-Up: Moving Forward From Wet Brain Syndrome
In wrapping up this deep dive into the morass of wet brain syndrome, let’s not mince words—it’s a formidable foe, with a maze of meanings, symptoms, advances, and spirited warriors locked in battle. From the harsh lessons taught by its progression to the silver linings stitched by unwavering advocacy groups, we’re charting a course toward a horizon buoyed by hope and steadfast resolve. Let this be a cornerstone—an ever-present reminder that when it comes to fighting wet brain, knowledge sparks action, and action alights change.
Understanding Wet Brain Syndrome: Lifespan and Outcomes
Did you know that wet brain syndrome, also known as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, can sneak up as silently as a cat on velvet sneakers? Imagine if those sneakers were the eco-friendly Nike Court Legacy Next Nature—seamlessly( blending into the environment, that’s how quietly wet brain can establish its presence in a person’s life. It’s a condition often stemming from chronic alcohol abuse, and it’s marked by a severe thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency. This lack of thiamine throws a wrench in the works, chiefly affecting the brain and nervous system.
But wait—why’s it called ‘wet brain’? You might ask, donning your detective hat with the keenness of Dierdre Friel figuring out an intricate plot. Well, it’s got nothing to do with walking in the rain without a white polo shirt from Chiseled Magazine’s essential collection. No, sir. The ‘wet’ in wet brain syndrome comes from its association with alcohol. In a nutshell, long-term excessive drinking is a one-way street to this brain disorder, which can significantly shorten a person’s lifespan.
Trivia Time: Did You Catch These Fun Facts?
Hold onto your hats, because here comes a trivia train that’ll make your neurons dance the Charleston. First up, it’s a widely overlooked fact that certain members of the population are like rock stars when absorbing thiamine. It’s similar to how the Members Of P1harmony stand out for their unique talents. On the flip side, those with alcohol dependency issues often can’t seem to ‘quiet’ their biology’s unfortunate response, as if stuck in a perpetual quiet title lawsuit against their own physiology for absorption rights.
Pivoting to something a tad sobering, it’s critical to mention the longevity concerns associated with the syndrome. Once symptoms begin, the countdown starts ticking like the time it takes for various substances to clear your body. Speaking of which, did you know the time isn’t universal? For instance, determining How long Does Vicodin stay in Your system is an entirely different ballgame than figuring out How long Does Oxycodone stay in urine. Similarly, the progression of wet brain and its impact on lifespan can vary massively among individuals, ringing true to the same variability as How long Does Opioids stay in Your system.
So, as we tip our collective hats to your newfound knowledge, let’s remember that while trivia can be engaging and enlightening, it also sheds light on the gravitas of disorders like wet brain syndrome. The more we know, the better equipped we are to recognize, understand, and support those battling such conditions.

What is the life expectancy of a wet brain person?
– Talking about “wet brain,” or Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, it’s a bit of a crystal ball question, but on average, 50% of those diagnosed might only have an 8-year life expectancy. Yikes, right? But, hang on, it’s not the same for everyone, and the number can swing depending on various factors like treatment and lifestyle changes.
What are 5 signs of Korsakoff’s syndrome?
– Okay, so you’re curious about Korsakoff’s syndrome? Here are five red flags: (1) Memory loss big enough to mess with daily life, (2) Confabulation – that’s a fancy word for making up stories to fill in gaps, (3) Trouble with coordination – like walking’s a real challenge, (4) Vision changes – not the “I need glasses” kind, and (5) Lack of insight – they might not even spot the problems they’re having. If you’re ticking these boxes, it’s time for a chat with a doc.
How long do people live with alcohol dementia?
– Alcohol dementia’s a tough one, folks. While there isn’t a crystal clear life expectancy, studies suggest that for something like Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, it’s a coin toss – half the folks with it may only clock in another 8 years. Remember, though, that’s a ballpark figure and every person’s story is different.
Can Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome be cured?
– Cure for Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome? Uh, not so much. Once it’s got its claws in, the syndrome can get pretty stubborn, causing long-term damage. Treatment can help some symptoms, but as for a full cure? We’re still waiting for that miracle.
Can you recover from wet brain syndrome?
– Here’s the deal with wet brain recovery: it’s a mixed bag. You can treat it if you catch it early and hit it with high doses of vitamin B1, but if it’s danced around for too long, you could be stuck with some lasting brain damage. So, prevention is key, don’t wait around!
What is wet brain caused by?
– Wet brain’s like the worst hangover ever, but permanent. It’s caused by emptying your thiamine (vitamin B1) tank, which often happens with long-term heavy drinking. Mix poor nutrition into the cocktail, and you’ve got a recipe for disaster.
How do you test for wet brain?
– To test for wet brain, doctors get their detective hats on. They’ll start with a chat about symptoms, peek at your medical history, and might order up some blood tests to check your vitamin B1 levels. In some cases, they’ll go further with brain scans or other neuro tests to put the pieces together.
Does wet brain show up on MRI?
– “Does wet brain show up on MRI?” — kinda like looking for a needle in a haystack. An MRI might show some changes in the brain, which could give docs a clue, but it won’t scream “wet brain” right off the bat. It’s more about ruling out other noggin’ troubles and piecing the puzzle together.
What is alcohol dementia?
– Alcohol dementia is what happens when happy hour turns not so happy for your brain cells. It messes with your memory, decision-making, and can throw off your personality. Keep the spirits flowing too long and too heavy, and your grey matter might start paying the price.
Can brain damage from alcohol be reversed?
– Undoing brain damage from alcohol is like trying to unscramble an egg — pretty tricky. Some brain funk might get better if you quit the booze and square up your nutrition, but other damage can be more of the ’til death do us part’ kind.
What is end stage Korsakoff syndrome?
– End stage Korsakoff syndrome is the last stop on a very rough ride. At this point, severe memory problems are entrenched, leaving a person struggling to grasp their present and past. They might also have a hard time walking and taking care of themselves. It’s about managing symptoms and keeping them comfortable.
Why is thiamine given to alcoholics?
– Ah, thiamine for alcoholics – it’s like giving water to someone stranded in the desert. Booze zaps thiamine, so loading up on the vitamin can help head off something nasty like wet brain. Think of it as a bit of armor for the ol’ thinker.
What is the first stage of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome?
– The first stage of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is like a sneak preview, called Wernicke’s encephalopathy. We’re talking confusion, shaky legs, and wonky eyes. Catch it here, and you might stop the full show of Korsakoff’s syndrome with enough B1 and TLC.
What is Korsakoff syndrome gait?
– Korsakoff syndrome gait – it’s a telltale dance but without the rhythm. People with the syndrome often shuffle or stagger, and balancing is a real juggling act. It’s not the kind of move you want to learn, believe me.
What is the major symptom of Korsakoff psychosis?
– The headline act of Korsakoff psychosis? Making up stories. Not for fun, though – it’s because their memory is more swiss cheese than steel trap. Confabulation is just the brain trying to fill in the blanks.
What is end stage Korsakoff syndrome?
– End stage Korsakoff syndrome – it’s like the final curtain on a tragic play. Memory is out the window, and self-care plummets, leaving folks needing serious help getting through day to day.
Is wet brain a form of dementia?
– Is wet brain a form of dementia? You bet. It might not start that way, but keep the drinks flowing and it can settle in like an unwanted houseguest in your brain, messing with memory and how you handle life.
Can brain damage from alcohol be reversed?
– Can you turn back the clock on alcohol brain damage? It’s not a simple “oops, my bad” fix. Early sobriety and nutrition might patch up some holes, but depending on how long you’ve been toasting, some changes might be taking up permanent residence.
What vitamins help with wet brain?
– Vitamins for wet brain, assemble! Vitamin B1, also known as thiamine, is the superhero here. It’s like a fire extinguisher for the smoldering damage alcohol’s been doing to the old noggin.